Overview
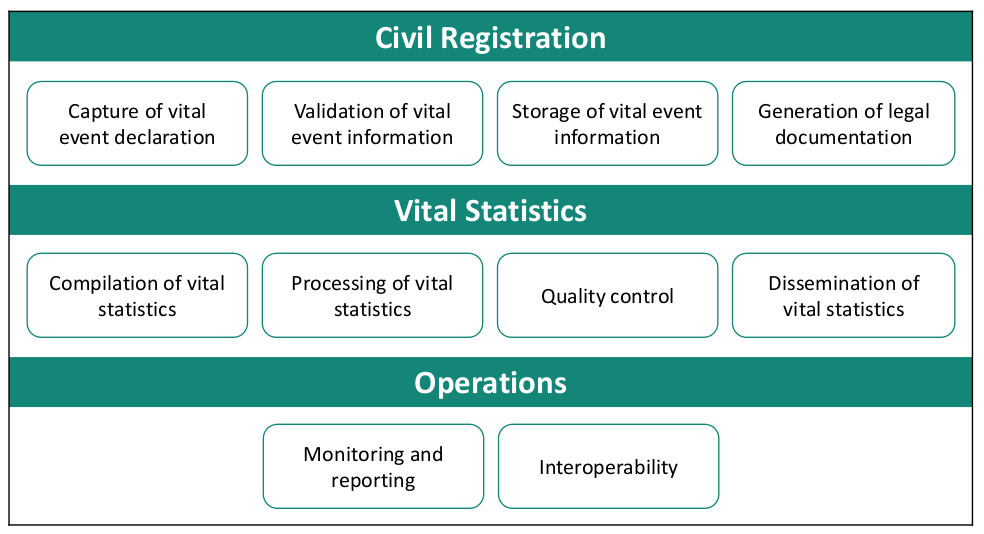
In order to identify appropriate technologies to support CRVS, an “As-Is” assessment must be conducted to understand the strengths and weaknesses of the existing CRVS Landscape, including several components documented in the Business Architecture e.g. CRVS business processes. Basing subsequent technology decisions on these findings will ensure that technology interventions directly address identified weaknesses. Note. If a Comprehensive Assessment has been conducted this should be used as an input to complete the below steps.
Steps:
1
Identify relevant stakeholders to be consulted and involved throughout the As-Is assessment, as identified in the RACI Matrix developed in Analysis & Design 1.
2
Assess the CRVS business processes documented in the previous activity, considering their effectiveness during “Business as Usual” and emergency situations (natural and conflict).
- Identify all process bottlenecks, inefficiencies, delays and informal practices, consulting stakeholders involved in the current CRVS process.
- Assess the capacity of actors to conduct current process steps, consulting stakeholders involved in the current CRVS process.
- Identify registration barriers i.e. reasons why citizens do not actively register vital events, consulting a representative sample of citizens and those involved in administering the current CRVS process.
- Annotate the business process flow diagrams with identified process bottlenecks and registration barriers. See Country Business Process Assessment Examples in the Toolbox.